Risk Adjustment Overview
A Practical Guide to HCC, RAS, and Manual Risk Scoring (V28)
September 30, 2025
FAQs
-
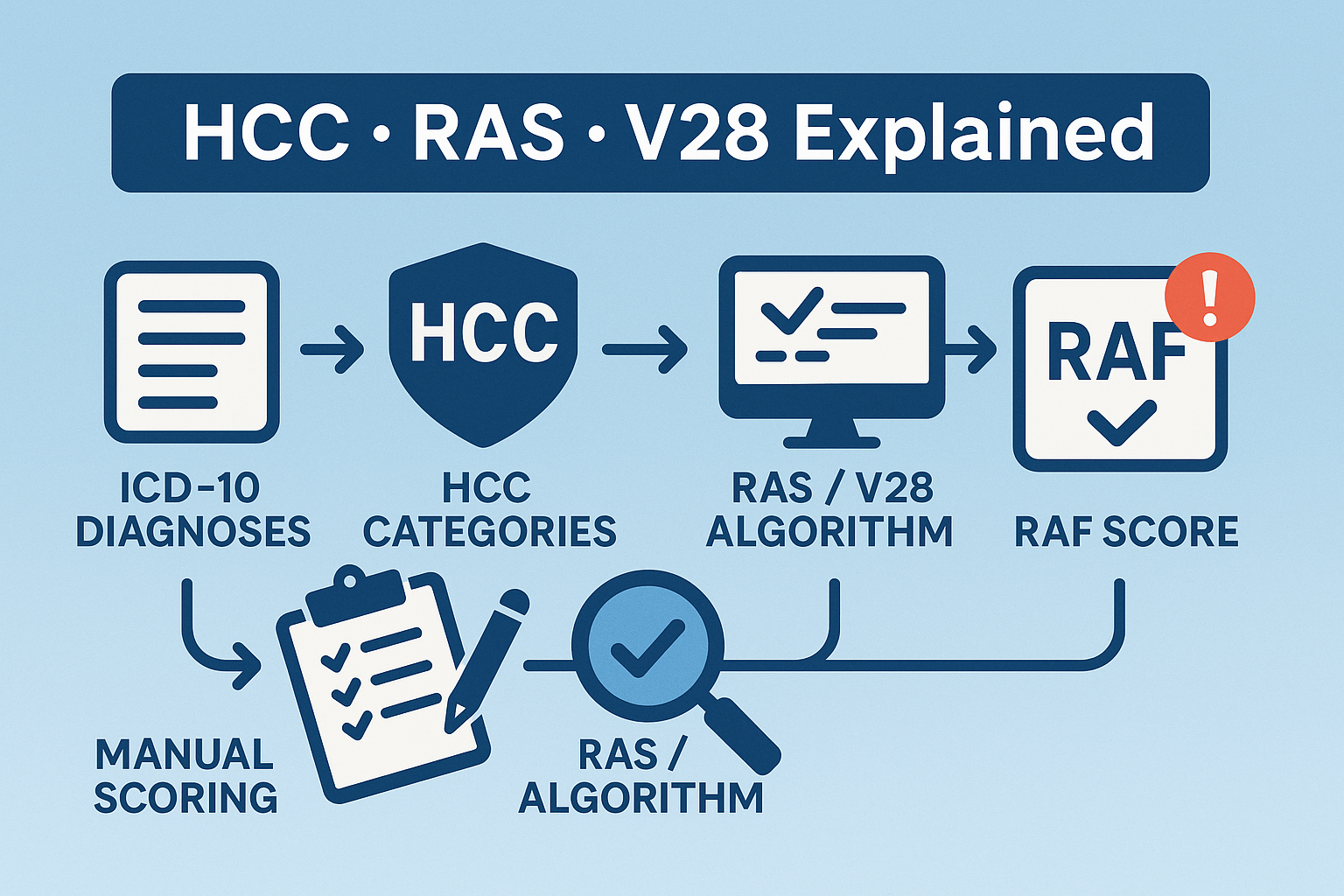
Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCCs) are diagnostic groupings that CMS uses to predict a member’s future healthcare costs. Each HCC represents a set of clinically related ICD-10 codes. When a provider documents and submits a diagnosis, it maps to an HCC that contributes to the member’s Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF). More severe or complex conditions increase the RAF, resulting in higher payments to the Medicare Advantage plan to reflect expected cost of care.
-
CMS-HCC Model V28 updates diagnosis mappings, payment HCC counts, and coefficients to better align payments with real-world data. Compared to earlier models (like V24), V28:
Expands the number of payment HCCs (≈ 115 vs 86).
Introduces constraining—where related HCCs share coefficients—to reduce volatility.
Adjusts normalization and coding pattern factors annually.
This means RAF calculations and payment projections under V28 may differ from past years, so payers must update mapping logic and re-validate coefficients to avoid revenue variance.
-
CMS receives diagnosis data from three main sources:
RAPS (Risk Adjustment Processing System): The legacy submission channel still used by PACE and some specialized populations.
EDPS (Encounter Data Processing System): The primary source for Medicare Advantage, capturing encounter-level details directly from plans.
FFS / IDR (Fee-for-Service / Integrated Data Repository): Used for beneficiaries moving between MA and FFS coverage.
CMS consolidates diagnoses from these sources to generate payment-year RAF scores.
-
Starting in CY 2026, CMS will begin transitioning official risk-adjustment model software from SAS to Python. Payers should:
Review CMS’s published Python model documentation.
Test dual-environment workflows (SAS + Python) during 2026 mid-year runs.
Ensure IT and actuarial teams can integrate Python output into existing validation pipelines.
Validate results against current SAS calculations to confirm accuracy before 2028, when Python becomes the sole supported format.
-
All official mapping, coefficient, and normalization files are available on the CMS Risk Adjustment Model Software page under Model Software & ICD-10 Mappings for each year.
Visit the CMS Risk Adjustment Model Resources →
You can also access summaries and quick-links in the HealthDataMax Knowledge Base → “CMS Model Files & Resources” section.